CLEM - Correlative Light and Electron Microscopy Solutions
Imagine that you can easily bridge the gap between the micrometer and nanometer scale, connecting functional and ultrastructural information. For a specific research question, this means employing different sample-preparation and microscopy techniques to combine multiple modalities, such as live-cell imaging, high-pressure freezing, ultramicrotomy, and (cryo) electron microscopy. A CLEM approach helps to bridge this gap.
CLEM solutions from Leica Microsystems ensure sample viability, quality checks, and a precise and reliable 3D targeting mechanism. Users can take advantage of these solutions to identify directly the right cell at the right time, obtain high-resolution cryo-confocal data, or put the fluorescence information into the ultrastructural context.
Our experts on solutions for Correlative Light and Electron Microscopes are happy to help you with their advice.
What CLEM is used for?
A CLEM approach is used for further investigation of a sample with sub-nanometer resolution, not only enabling the combination of different layers of information from one region, but also specific targeting of a region of interest in the bulk - just like having a lighthouse when wondering in the dark.
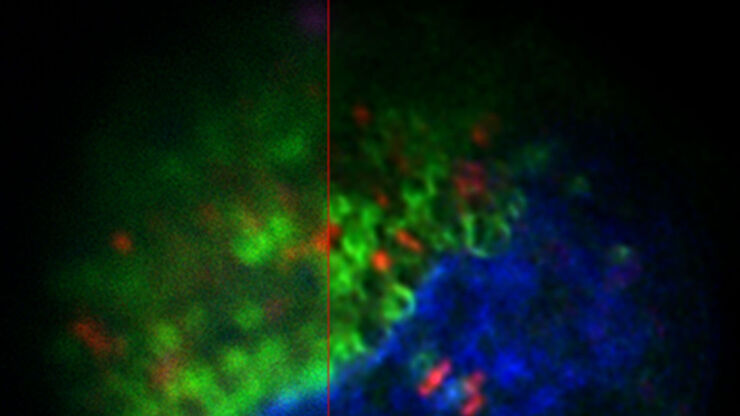
For example, a labeled protein can be easily detected and targeted by cryo-fluorescence microscopy for further protein-structure analysis using cryo-EM (read more about Coral Cryo). Another example is when you wish to combine dynamic information (e.g., cell-cell interaction) with structural information and go beyond the limit of light resolution (read more about Coral Life).
However, as easy as it sounds, there are many challenges in creating a smooth and successful (cryo) CLEM workflow. Already in the experimental design stage, users should consider addressing the following questions:
- How to prepare and maintain the sample in an optimal state?
- How to identify and mark target structures of interest?
- How to transfer the sample safely and efficiently between instruments?
- How to provide the imaging and target data in a suitable format for subsequent EM steps?
The Coral family helps you to handle your sample, step by step, ensuring a higher reliability of your CLEM workflow.
How are CLEM data correlated?
Correlation of Light and Electron Microscopy is crucial for a successful experiment, both for room temperature and cryo-CLEM experiments. Coordination systems must be established and well recognized with different imaging modalities. Imaging information is then overlayed by either image fit (for large overview data) or absolute coordination of positions (x,y,z, values) for retrieving high-resolution information with high precision.
What is Cryo-CLEM?
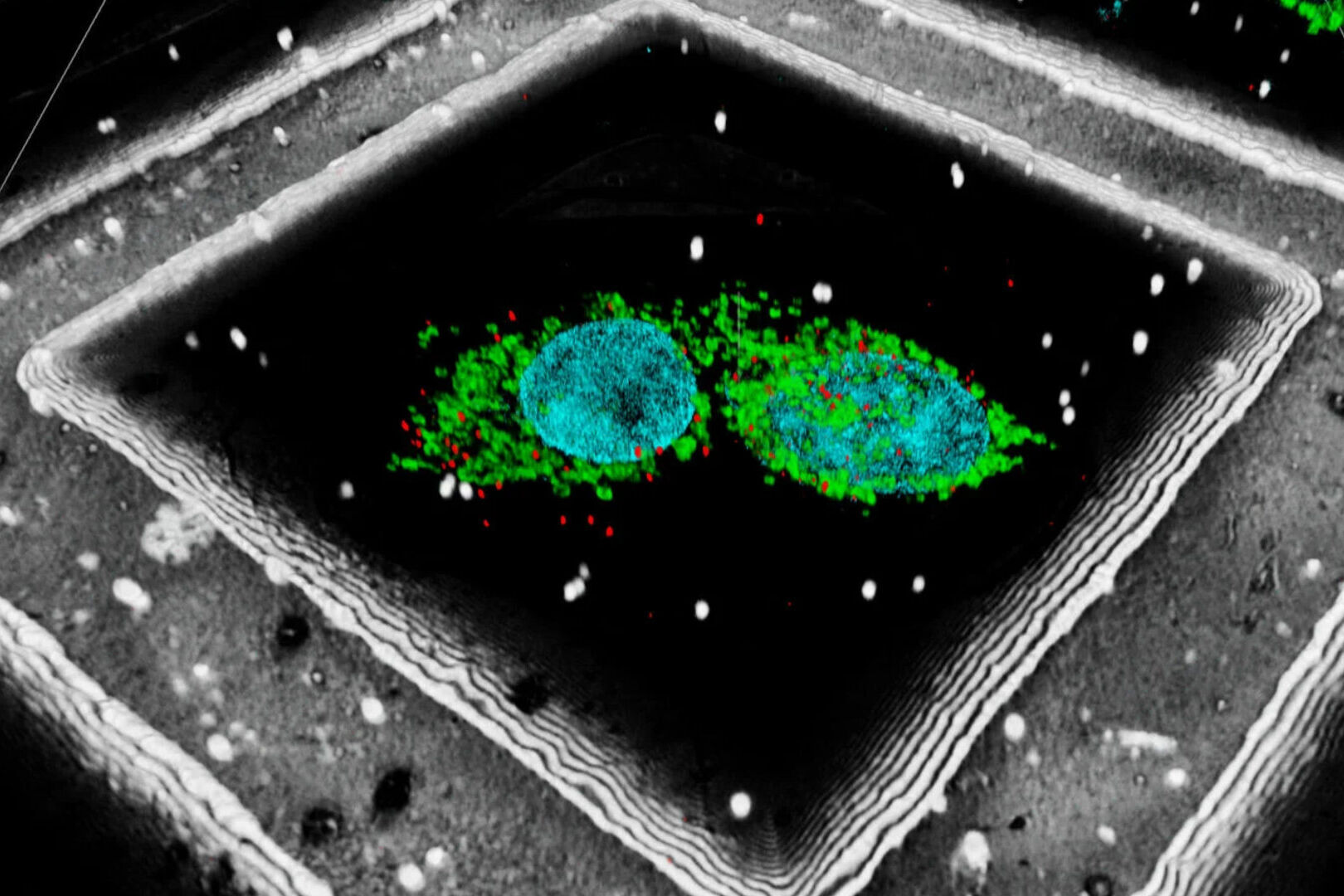
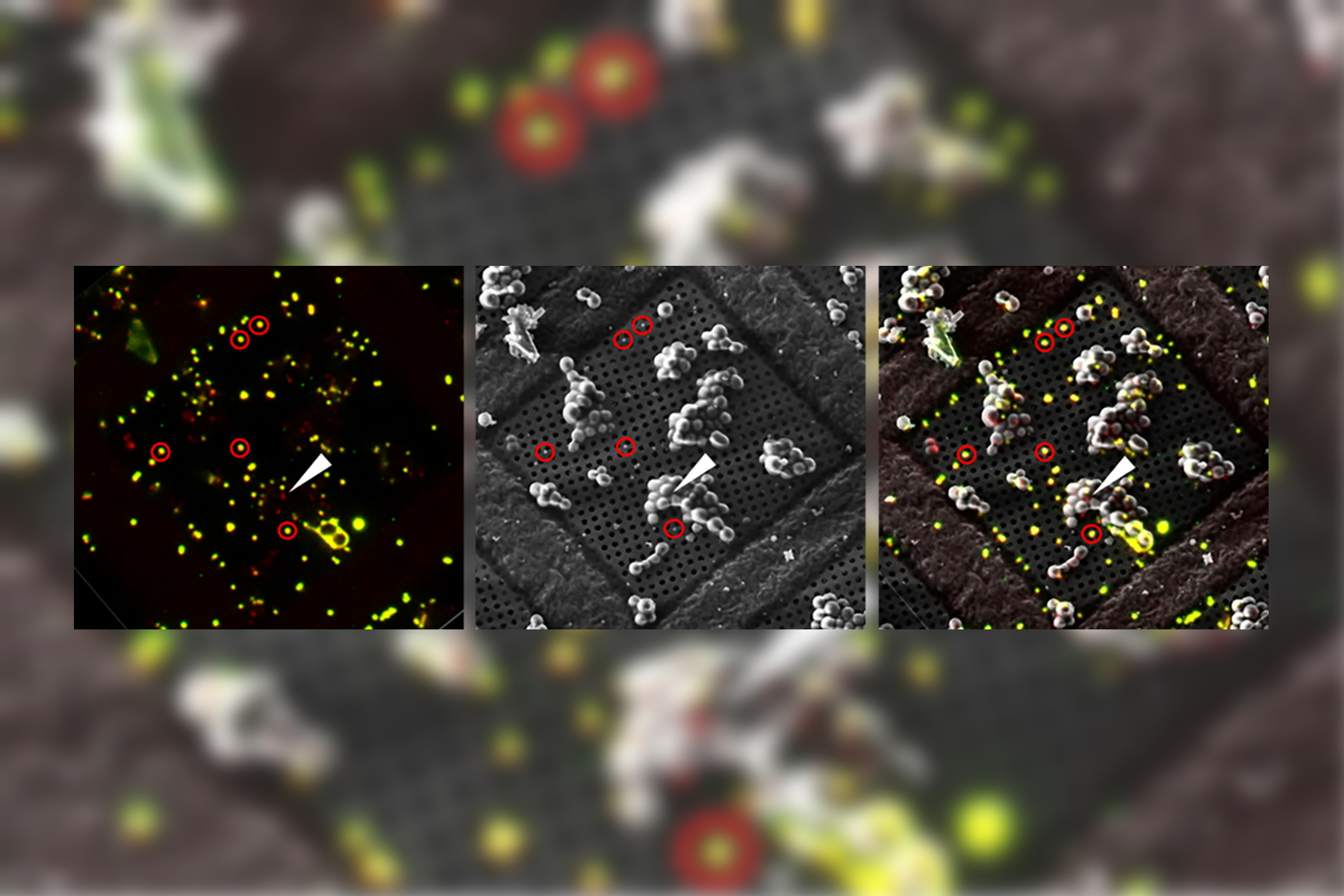
In Cryo-CLEM (correlative light and electron microscopy), both imaging steps are performed under cryogenic conditions which implies the need for a reliable cryo-sample-preparation workflow. This includes reliable sample vitrification, safe sample transport and stable cryo-light imaging. Special attention should be given to ice contamination: high humidity environments and dirty LN2 can easily put your sample at risk. Coral Cryo provides: 1) A safe and clean handling of your samples; 2) Stable and long-term cryo-light imaging; and 3) Imaging and precise targeting of biomolecules within their native environment using the Coral Cryo software.
Introducing Coral Life workflow
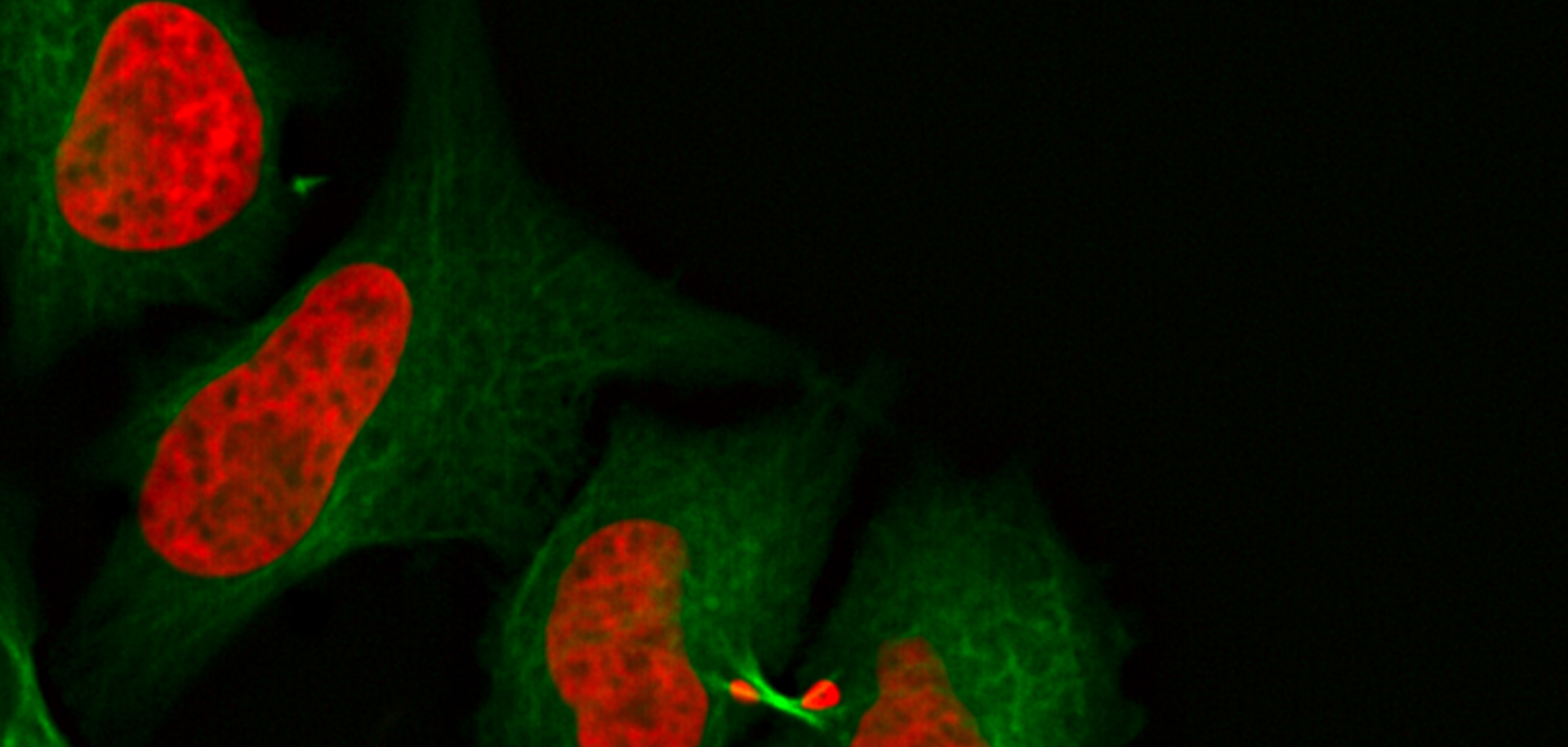
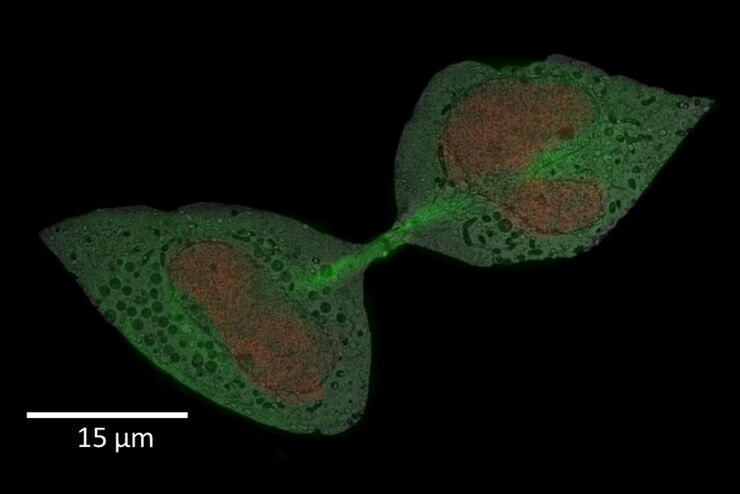
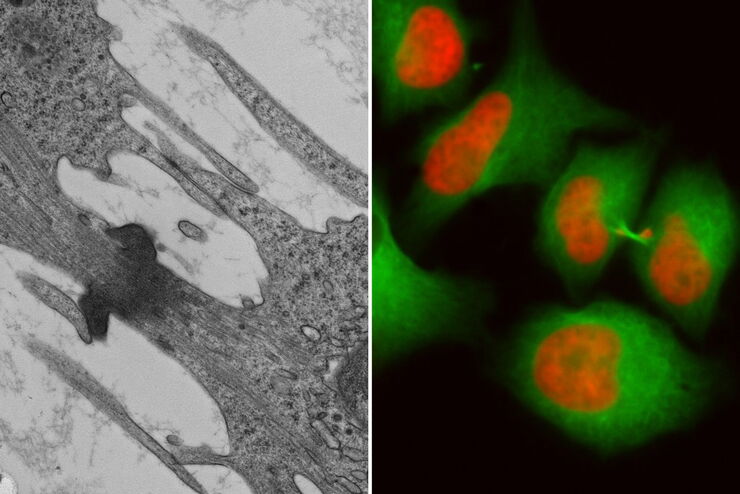
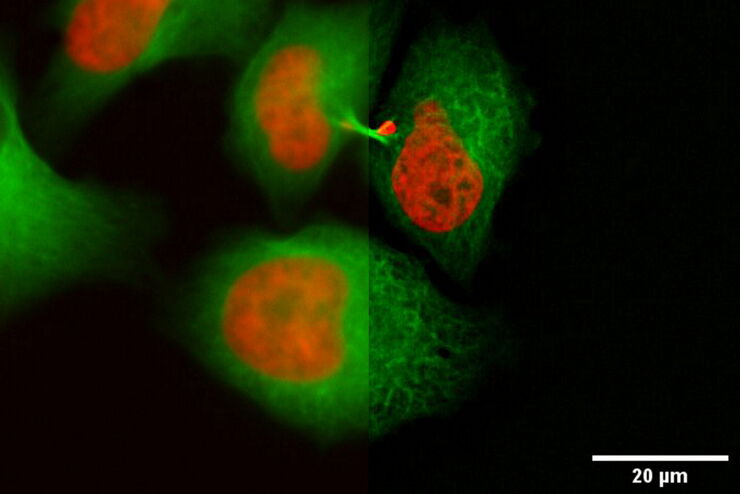
Fluorescence live-cell imaging is a widely used way of visualizing cellular processes over time. However, there are cases when information retrieved by light microscopy is simply not enough to provide insights on cellular mechanisms. In that case, an absolute, ultrastructure image in high resolution, provided by (RT) EM, is required.
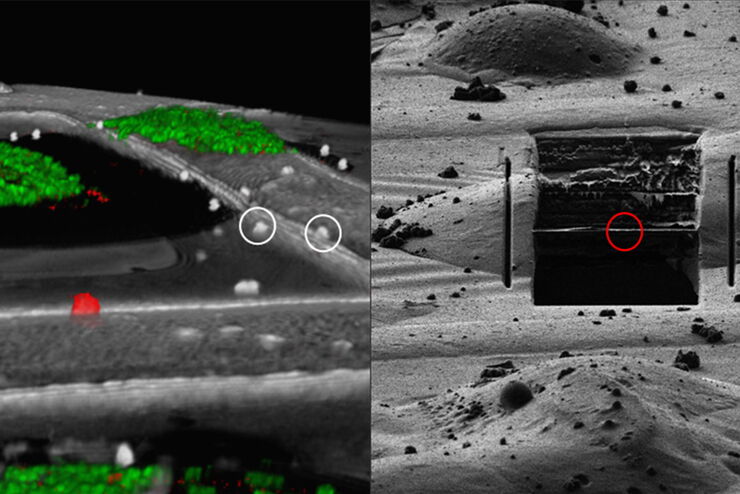
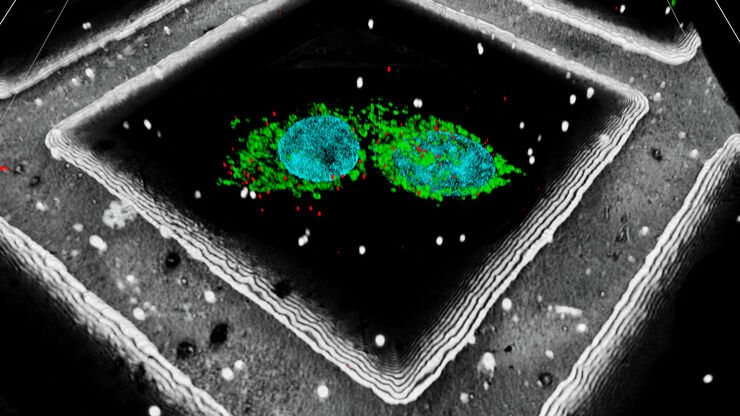
Leica Microsystems’ Coral Life workflow allows you to track and image rare cellular events over time using fluorescent microscopy in a physiologically safe environment . Once the event of interest takes place, you can vitrify your sample within only five seconds for further analysis in RT EM (TEM, SEM, FIB/SEM).
It streamlines sample transfer from carefully maintained cell-culture environments to fluorescence imaging and fast vitrification by high-pressure freezing. The Coral Life live-cell-to-vitrification workflow makes it possible to capture rare-cell events when they happen making them available for EM analysis.
Introducing Coral Cryo workflow
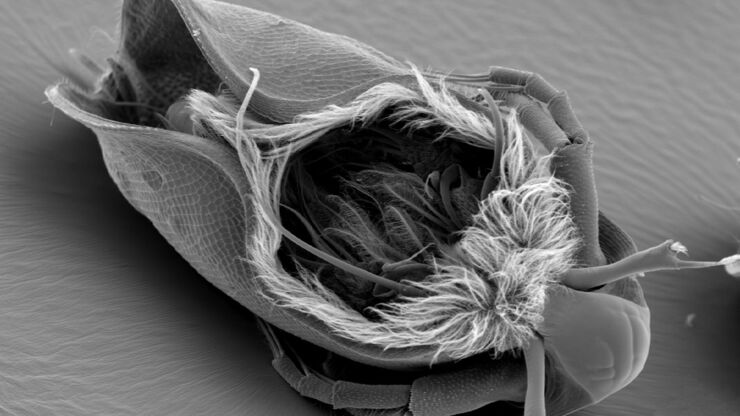
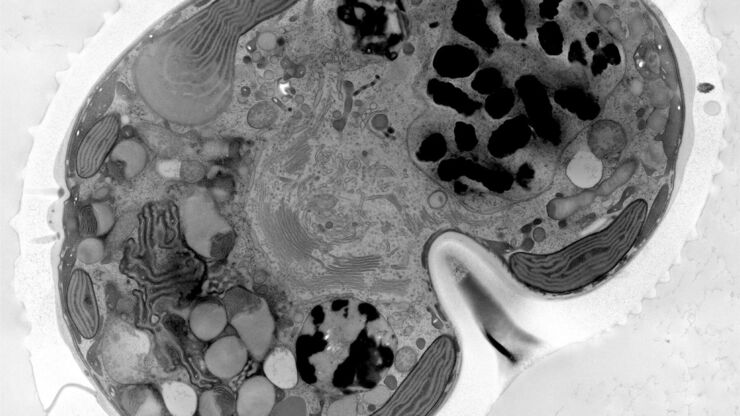
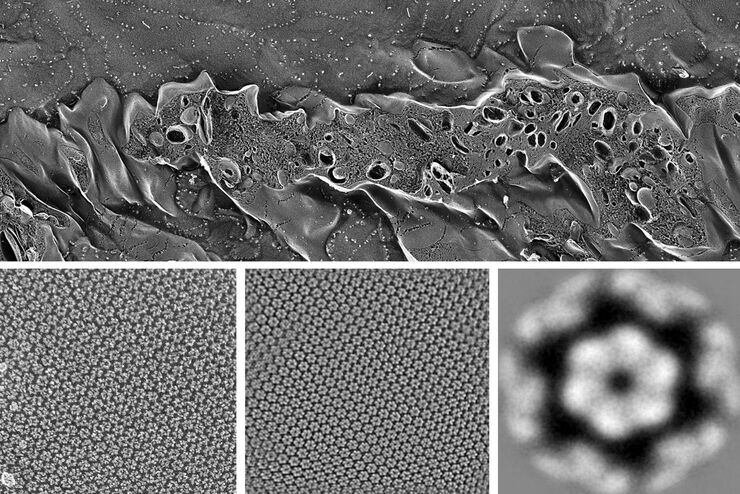
Cryo-electron microscopy has become one of the most important techniques for structural biology. It allows elucidation of a protein structure in its native, often multi-conformational state – an insight that X-ray crystallography cannot provide.
The ability to combine the ultra-structural data, coming from Cryo-EM, with the high-precision confocal targeting, obtained using the STELLARIS Cryo, provides a powerful Cryo-CLEM method. Coral Cryo, the cryo correlative light and electron microscopy workflow by Leica Microsystems, optimizes hardware and software to provide a smooth transition between the two imaging modalities.
Together with our comprehensive portfolio for Cryo-EM sample preparation, Coral Cryo addresses the growing needs within the Cryo-CLEM and Cryo-ET community to increase the success rate of these type of experiments.
Related Articles
Interested to know more?
Talk to our experts.
Do you prefer personal consulting? Show local contacts