22
–
23
Apr
2025
第四届半导体封装检测及失效分析技术进展网络研讨会
China
•
Webinar
22
Apr
2025
共聚焦荧光寿命成像功能在植物相关研究中的应用
China
•
Webinar
Filter articles
标签
产品
Loading...
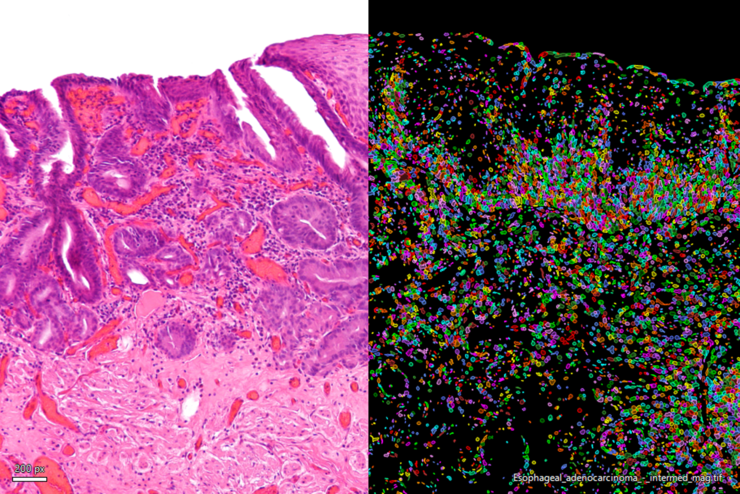
人工智能显微图像分析-介绍
人工智能引领的显微图像分析和可视化是用于数据驱动型科学发现的一项强大工具。人工智能技术可以帮助研究人员应对具有挑战性的成像应用,让他们能够从图像中获取更多的信息。
Loading...
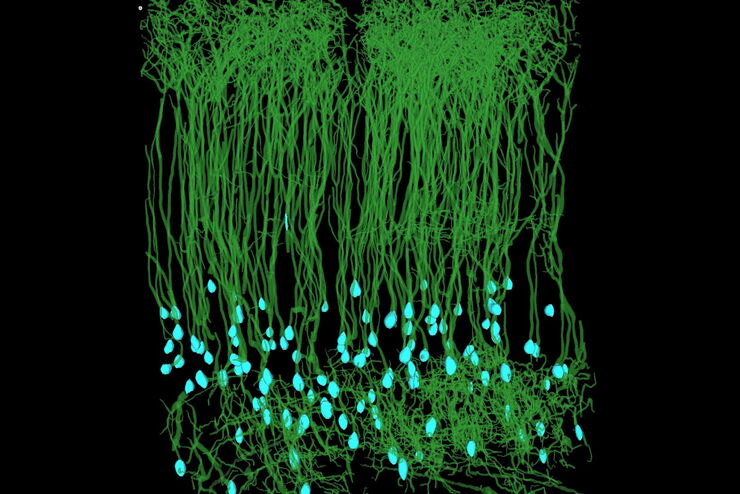
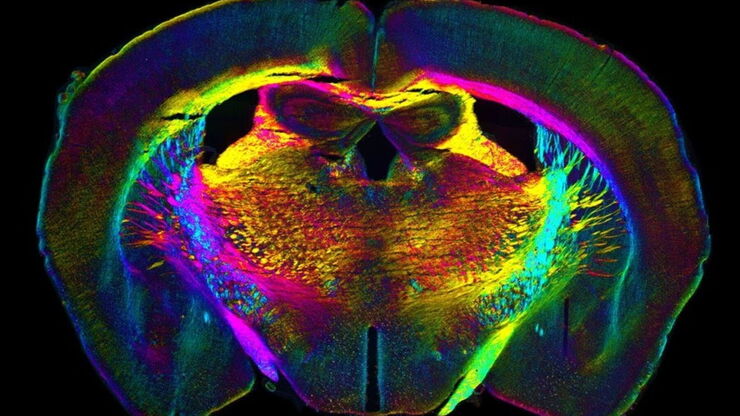
自动化加速神经元图像分析
复杂神经投射的检测能力主要取决于大规模神经元网络的精确重建。神经科学研究中的大多数数据析取方法都非常耗时和易错,进而导致进度延误和错误。在本次研讨会中,Aivia将演示如何利用自动化技术提升图像分析工作流的效率
Loading...
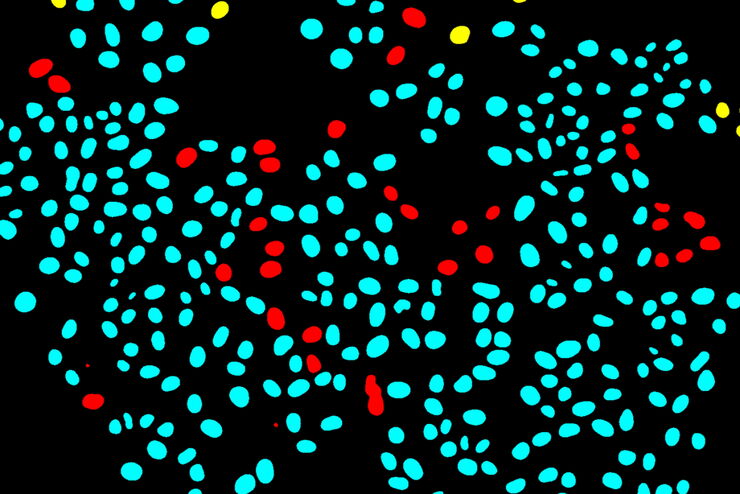
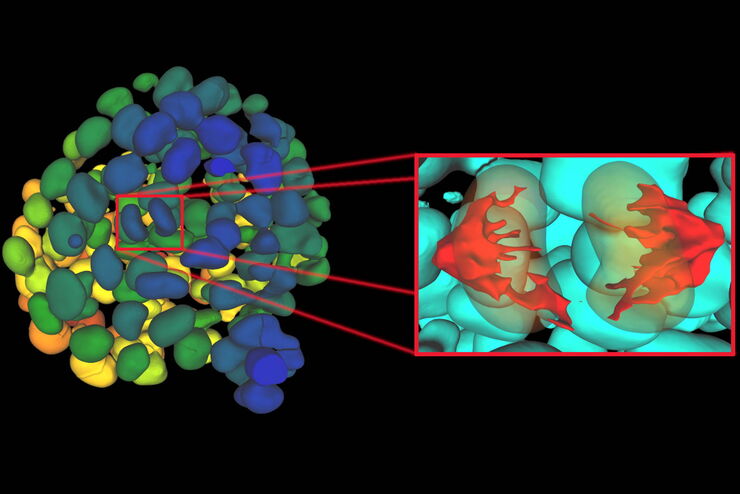
使用深度学习技术追踪单细胞
人工智能解决方案在显微镜领域的应用不断拓展。从自动化目标分类到虚拟染色,机器学习和深度学习技术在帮助显微镜学家简化分析工作的同时,也在持续推动科学技术领域的突破。