Filter articles
标签
产品
Loading...

组织中的精密空间蛋白质组学信息
尽管可使用基于成像和质谱的方法进行空间蛋白质组学研究,但是图像与单细胞分辨率蛋白丰度测量值的关联仍然是个巨大的挑战。最近引入的一种方法,深层视觉蛋白质组学(DVP),将细胞表型的人工智能图像分析与自动化的单细胞或单核激光显微切割及超高灵敏度的质谱分析结合在了一起。DVP在保留空间背景的同时,将蛋白丰度与复杂的细胞或亚细胞表型关联在一起。
Loading...

A Guide to Spatial Biology
What is spatial biology, and how can researchers leverage its tools to meet the growing demands of biological questions in the post-omics era? This article provides a brief overview of spatial biology…
Loading...

An Introduction to Laser Microdissection
The heterogeneity of histological and biological specimens often requires isolation of specific single cells or cell groups from surrounding tissue before molecular biology analysis can be carried…
Loading...
![[Translate to chinese:] Mouse brain (left) microdissected with a 10x objective (upper right). Inspection of the collection device (lower right). [Translate to chinese:] Mouse brain (left) microdissected with a 10x objective (upper right). Inspection of the collection device (lower right).](/fileadmin/_processed_/f/3/csm_Mouse_brain_microdissected_with_10x_objective_5fbd8963bf.jpg)
激光微切割(LMD)促进的分子生物学分析
使用激光微切割(LMD)提取生物分子、蛋白质、核酸、脂质和染色体,以及提取和操作细胞和组织,可以深入了解基因和蛋白质的功能。它在神经生物学、免疫学、发育生物学、细胞生物学和法医学等多个领域有广泛应用,例如癌症和疾病研究、基因改造、分子病理学和生物学。LMD 也有助于研究蛋白质功能、分子机制及其在转导途径中的相互作用。
Loading...
![[Translate to chinese:] Brightfield image of a pig liver stained with hematoxylin-eosin (HE). [Translate to chinese:] Brightfield image of a pig liver stained with hematoxylin-eosin (HE).](/fileadmin/_processed_/1/3/csm_Pig_Liver_BF_stained_with_hematoxylin-eosin_b2c110c09d.jpg)
空间代谢组学:探索肿瘤复杂性和治疗见解
在癌症研究中,理解肿瘤细胞与其微环境之间的相互作用至关重要,因为肿瘤微环境显著影响肿瘤进展。空间代谢组学是一种由研究人员开发的新方法,用于研究这一复杂性。通过揭示肿瘤微环境中的空间变化,该方法提供了对其多样化成分及其组织的宝贵见解。这些见解不仅影响临床结果,还为治疗反应提供信息,为个性化治疗策略铺平道路。
Loading...
![[Translate to chinese:] Mosaic scan of a Masson-Goldner stained cat brain. Magnification: 20x. [Translate to chinese:] Mosaic scan of a Masson-Goldner stained cat brain. Magnification: 20x.](/fileadmin/_processed_/4/d/csm_Cat_Brain_Masson-Goldner_20x_Mosaic_066f4f5801.jpg)
基于激光显微切割的稀疏细胞脂质组学分析
通过高覆盖率靶向脂质组学分析稀疏细胞,深入探讨细胞复杂性。这种先进的方法结合了激光显微切割(LMD)和液相色谱-质谱/质谱(LC-MS/MS),揭示了单细胞水平的代谢变化,阐明了糖尿病和肥胖等疾病。通过采用激光显微切割(LMD)获得无污染样本,并使用 SCIEX 7500 系统提高灵敏度,该方法成功检测到 285…
Loading...
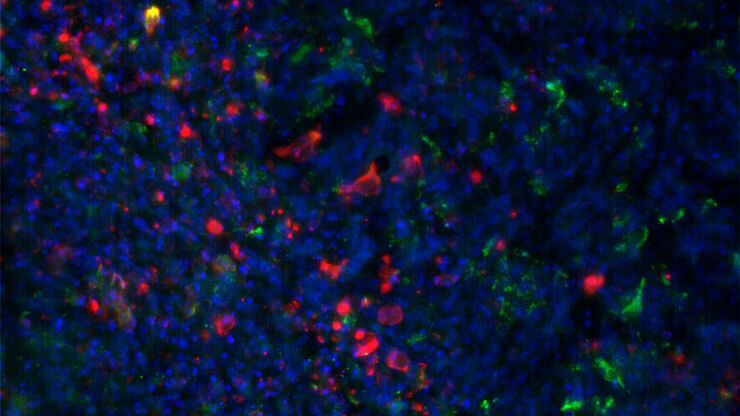
![[Translate to chinese:] Image of murine dopaminergic neurons which have been marked for laser microdissection (LMD). [Translate to chinese:] Image of murine dopaminergic neurons which have been marked for laser microdissection (LMD).](/fileadmin/_processed_/b/f/csm_Murine_dopaminergic_neurons_marked_for_LMD_d784dbd83f.jpg)
利用激光显微切割(LMD)在空间背景下分离神经元
在阿尔茨海默病之后,帕金森病是第二常见的进行性神经退行性疾病。在首发症状出现之前,中脑中高达70%的多巴胺释放神经元已经死亡。本文描述了如何使用现代激光显微切割(LMD)方法帮助解决帕金森病之谜。研究涉及在空间背景下分离和分析神经元。这些细胞来自帕金森病患者的死后黑质组织样本,以便深入了解该病的分子机制。
Loading...

激光显微切割技术如何助力神经科学研究取得开创性进展?
玛尔塔·帕特林尼博士,卡罗林斯卡学院的高级科学家,分享了她在成人人类神经发生开创性研究中使用激光显微切割(LMD)的经验,并提供了关于LMD在空间蛋白质组学和精准医学中未来应用潜力的个人见解。