Filter articles
标签
产品
Loading...
利用新型可扩展的干细胞培养设计未来
具有远见卓识的生物技术初创企业 Uncommon Bio 正在应对世界上最大的健康挑战之一:食品可持续性。在这次网络研讨会上,干细胞科学家塞缪尔-伊斯特(Samuel East)将展示他们如何使细胞农业的干细胞培养基既安全又经济可行。了解他们如何将培养基成本降低 1000 倍,并开发出不含动物成分、食品安全的 iPSC 培养基。
Loading...

组织中的精密空间蛋白质组学信息
尽管可使用基于成像和质谱的方法进行空间蛋白质组学研究,但是图像与单细胞分辨率蛋白丰度测量值的关联仍然是个巨大的挑战。最近引入的一种方法,深层视觉蛋白质组学(DVP),将细胞表型的人工智能图像分析与自动化的单细胞或单核激光显微切割及超高灵敏度的质谱分析结合在了一起。DVP在保留空间背景的同时,将蛋白丰度与复杂的细胞或亚细胞表型关联在一起。
Loading...
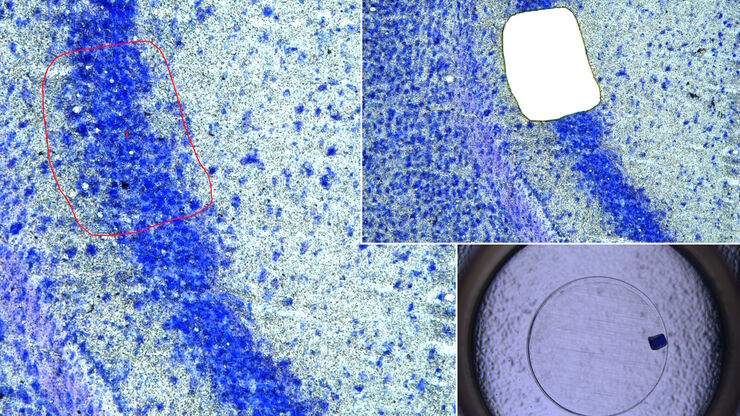
激光微切割(LMD)促进的分子生物学分析
使用激光微切割(LMD)提取生物分子、蛋白质、核酸、脂质和染色体,以及提取和操作细胞和组织,可以深入了解基因和蛋白质的功能。它在神经生物学、免疫学、发育生物学、细胞生物学和法医学等多个领域有广泛应用,例如癌症和疾病研究、基因改造、分子病理学和生物学。LMD 也有助于研究蛋白质功能、分子机制及其在转导途径中的相互作用。
Loading...

利用AI增强的细胞计数实现精准和高效
本文描述了利用AI进行精确和高效的细胞计数。准确的细胞计数对于 2D 细胞培养的研究至关重要,例如细胞动力学、药物发现和疾病建模。精确的细胞计数对于确定细胞存活率、增殖速率和实验条件的影响至关重要。这些因素对于可靠和稳健的结果至关重要。描述了基于人工智能的方法如何显著提高细胞计数的准确性和速度,从而对细胞研究产生重大影响。
Loading...

利用AI实现细胞转染的高效分析
本文探讨了AI(AI)在优化 2D 细胞培养研究中转染效率测量中的关键作用。对于理解细胞机制而言,精确可靠的 2D 细胞培养转染效率测量至关重要。靶向蛋白的高转染效率对于包括活细胞成像和蛋白纯化在内的实验至关重要。手动估计存在不一致性和不可靠性。借助AI的力量,可以实现高效可靠的转染研究。
Loading...

通过 AI 汇合度提高 2D 细胞培养的精度
本文解释了如何利用人工智能(AI)进行高效、精确的 2D 细胞培养汇合度评估。准确评估细胞培养的汇合度,即表面积覆盖的百分比,对于可靠的细胞研究至关重要。传统方法使用视觉检查或简单算法,使结果不客观和精确,尤其是对于用于药物发现、组织工程和再生医学的复杂细胞系。利用自动化图像分析和深度学习算法的方法提供更好的精度,并可以增强实验结果。
Loading...

采用徕卡THUNDER-DM6B观察SARS-CoV-2感染宿主细胞及其复制过程
冠状病毒2致重度急性呼吸综合征(SARS-CoV-2)
冠状病毒2致重度急性呼吸综合征(SARS-CoV-2)出现于2019年末,并快速传播全世界。由于其大面积的影响,研究人员对病毒的性质进行了深入的研究以期最终阻止大流行。一个重要的方面是病毒如何在宿主细胞中复制。Ogando及其同事的研究已经揭示了SARS-CoV-2的复制动力学、适应能力和细胞病理学。他们的工具之一是用荧光显微镜观察SARS…