Filter articles
标签
产品
Loading...

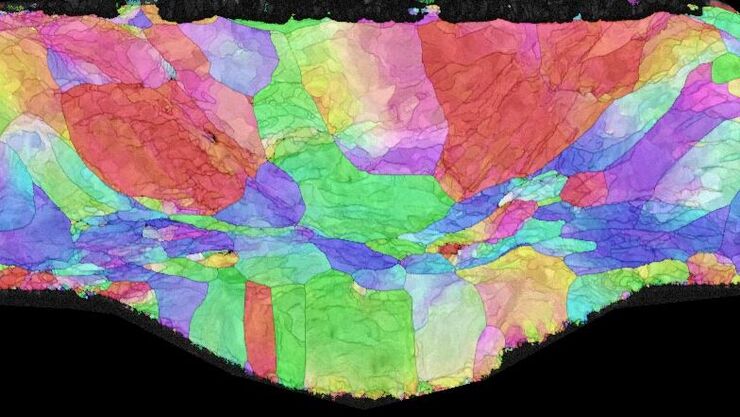
利用大数据探索阿尔茨海默病的空间蛋白组
阿尔茨海默病是一种遗传性和散发性的神经退行性疾病,导致中晚年认知能力下降,特征为β-淀粉样蛋白斑块和 tau蛋白 缠结。由于治疗选择有限,新的研究策略至关重要。Cell DIVE 多重成像解决方案可以对阿尔茨海默病脑组织进行研究,揭示,可能新的研究方向。这里我们展示了 Cell DIVE 多重成像仪的图像查看器,用户能够直接在自己的浏览器中访问完整的阿尔茨海默病多重数据集。
Loading...

Uncover the Hidden Complexity of Colon Cancer with Big Data
Colorectal cancer poses a significant health burden. While surgery is effective initially, some patients develop recurrent secondary disease with poor prognosis, necessitating advanced therapies like…
Loading...

Dive into Pancreatic Cancer Research with Big Data
Pancreatic cancer, with a mortality rate near 40%, is challenging to treat due to its proximity to major organs. This story explores the complex biology of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC),…
Loading...
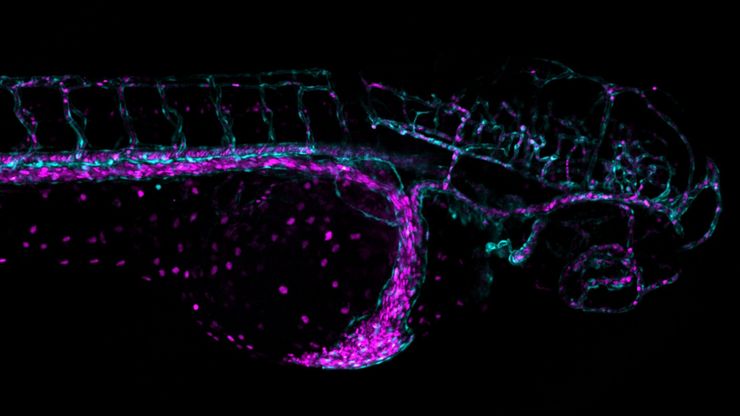
Overcoming Challenges with Microscopy when Imaging Moving Zebrafish Larvae
Zebrafish is a valuable model organism with many beneficial traits. However, imaging a full organism poses challenges as it is not stationary. Here, this case study shows how zebrafish larvae can be…
Loading...

如何在块面中自动获取感兴趣的荧光细胞
本文介绍了使用超薄切片超薄切片机自动修整修块功能,获取树脂块面中带有荧光信号的细胞结构。我们展示了如何使用配置有体视显微镜 M205 FA 的超薄切片超薄切片机 UC Enuity ,来识别感兴趣的荧光细胞,如何自动修整包含细胞的块面,以及如何在切片中观察细胞而无需转移到外部显微镜。
Loading...

An Introduction to Laser Microdissection
The heterogeneity of histological and biological specimens often requires isolation of specific single cells or cell groups from surrounding tissue before molecular biology analysis can be carried…
Loading...
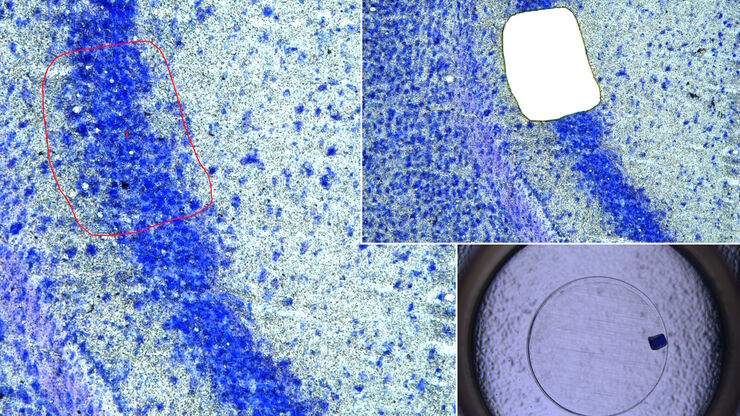
激光微切割(LMD)促进的分子生物学分析
使用激光微切割(LMD)提取生物分子、蛋白质、核酸、脂质和染色体,以及提取和操作细胞和组织,可以深入了解基因和蛋白质的功能。它在神经生物学、免疫学、发育生物学、细胞生物学和法医学等多个领域有广泛应用,例如癌症和疾病研究、基因改造、分子病理学和生物学。LMD 也有助于研究蛋白质功能、分子机制及其在转导途径中的相互作用。
Loading...

利用激光显微切割(LMD)在空间背景下分离神经元
在阿尔茨海默病之后,帕金森病是第二常见的进行性神经退行性疾病。在首发症状出现之前,中脑中高达70%的多巴胺释放神经元已经死亡。本文描述了如何使用现代激光显微切割(LMD)方法帮助解决帕金森病之谜。研究涉及在空间背景下分离和分析神经元。这些细胞来自帕金森病患者的死后黑质组织样本,以便深入了解该病的分子机制。