Filter articles
标签
产品
Loading...

优化 THUNDER 平台以实现高内涵玻片扫描
随着对全组织成像需求的不断增长以及对不同生物标本中 FL 信号定量的需要,HC 成像技术的极限受到了考验,而核心设备的用户可培训性和易用性则成为了成本和效率的问题。在这里,我们展示了在我们的设施中为THUNDER平台开发的可行工作流程,以支持从 KO-小鼠组织分析到人类癌症的各种研究环境需求。
Loading...
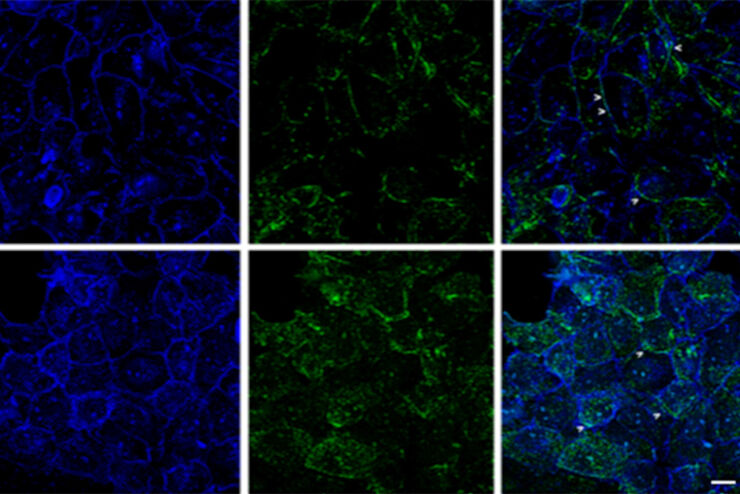
改进成像技术以了解细胞器膜细胞动态
了解正常组织和肿瘤组织中的细胞功能,是推动潜在治疗策略研究和了解某些治疗失败原因的关键因素。单细胞分析在生物医学研究中至关重要,它能揭示在癌症等复杂疾病中哪些细胞和分子通路发生了改变。
Loading...
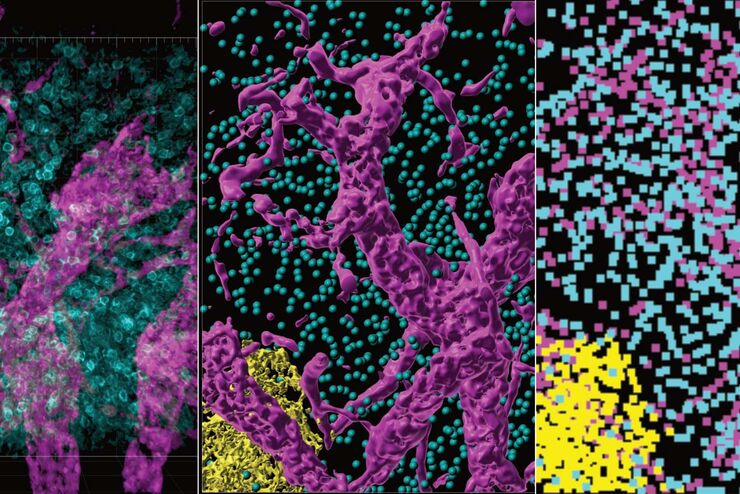
从器官到组织再到细胞:使用宽场显微镜分析 3D 标本
在传统的宽场显微镜下从厚的三维样本中获取高质量的数据和图像是具有挑战性的,因为存在失焦光的干扰。在本次网络研讨会中,Falco Krüger 展示了THUNDER成像仪如何通过Computational Clearing技术使这一切成为可能。
Loading...
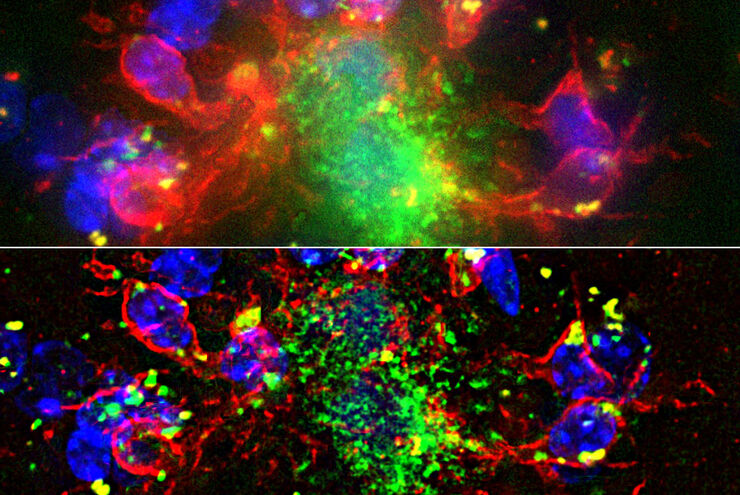
Computational Clearing - 增强3D标本成像
本次网络研讨会旨在阐明有助于THUNDER显微成像仪实现三维样品可视化的关键规格,并改进研究人员的成像相关工作流程。
Loading...
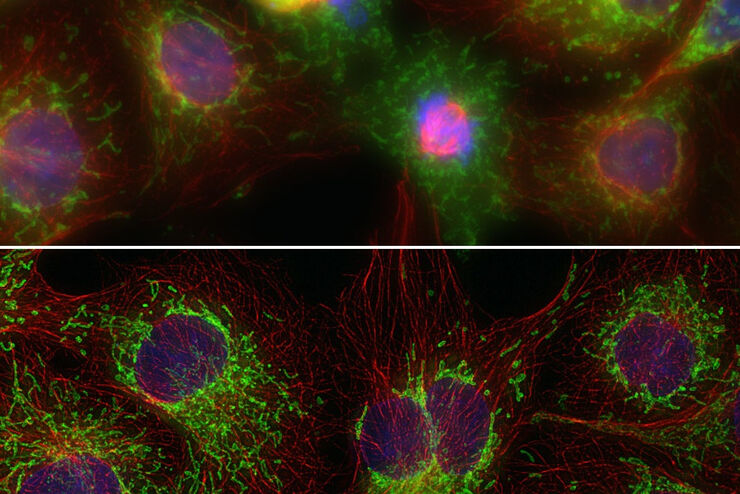
THUNDER成像:高效、灵活、易操作,让您的日常成像工作流更轻松
本次网络研讨会将展示 THUNDER 在许多不同生命科学应用中的多功能性和性能:从计数视网膜切片中的细胞核和癌组织切片中的 RNA 分子,到监测阿拉伯芥幼苗中的钙波等等。

