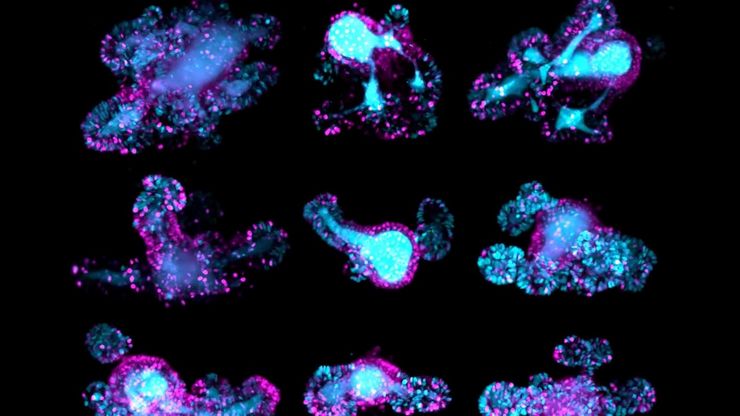
High-Pressure Freezing for Organoids: Cryo CLEM & FIB Lift Out
Master cryo EM workflow steps for challenging 3D samples: when to choose HPF vs. plunge freezing, reproducible blotting/ice control, contamination aware transfers, Cryo CLEM 3D targeting in organoids,…
Guide to Live-Cell Imaging
For a wide range of applications in various research fields of life science, live-cell imaging is an indispensable tool for visualizing cells in a state as close to in vivo, i.e. living and active, as…
高压冷冻简介
水是细胞最主要的组成部分,因此对于维持细胞超微结构至关重要。目前,冷冻固定是固定细胞成分,而不导致其显著结构变化的唯一途径。现阶段有两种常见的方法:投入冷冻与高压冷冻固定。
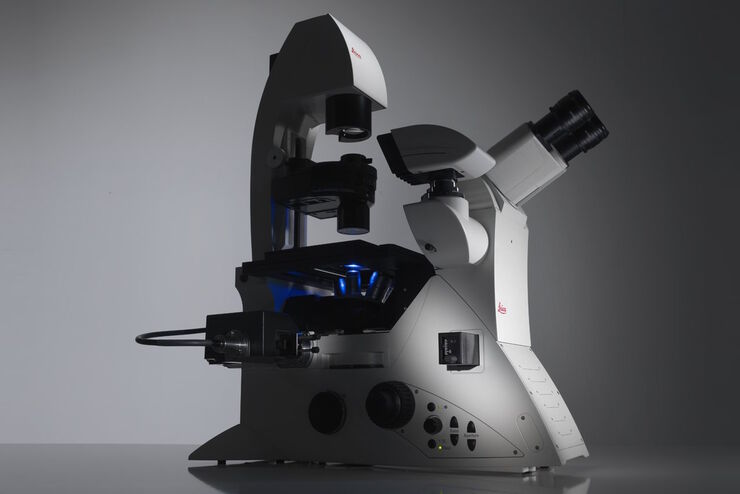
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Research Microscope
An optical microscope is often one of the central devices in a life-science research lab. It can be used for various applications which shed light on many scientific questions. Thereby the…
无限远光学系统 - 从 "无限远光学 "到无限远端口
"无限远光学 "是指显微镜的物镜和管状透镜之间的光路具有平行光线的概念 [1]。在这个 "无限远空间 "中放置平面光学元件不会影响图像的形成,这对于科学应用中常用的 DIC 或荧光等对比方法至关重要。需要在无限远光路中添加光源或激光设备等仪器。本文介绍了满足这一需求的不同方法。
人工智能与深度视觉蛋白质组学 (DVP) 相结合,推进疾病研究
在这次网络研讨会上,Andreas Mund 博士将介绍深度可视蛋白质组学(DVP)--一种将人工智能驱动的组织空间分辨、非靶向蛋白质组学相结合的尖端平台。他展示了 DVP 如何从最小的、表型匹配的细胞群中识别数千种蛋白质,并在复杂的临床组织样本中生成高分辨率分子图谱,从而在细胞水平上解码疾病机制。
用于二维细胞培养的显微镜和AI解决方案
这本电子书探讨了显微镜和AI技术在二维细胞培养工作流程中的整合。报告重点介绍了明视野、相衬和荧光等传统成像方法如何支持常规细胞监测,而 Mateo TL 和 Mateo FL 数字式倒置显微镜则通过自动汇合检查、细胞计数和转染分析提高了可重复性。它还展示了综合数据管理、审计跟踪和样本跟踪如何改进文档和研究的完整性。本书最后展望了未来趋势,包括微流控技术和 2D-3D…
人工智能驱动的乳腺癌研究多重染色成像空间分析工具
乳腺癌(BC)是女性因癌症死亡的主要原因,研究查肿瘤微环境(TME)对于阐明肿瘤进展机制至关重要。利用超多标染色空间蛋白质组学技术系统地绘制肿瘤微环境图谱可以提高精准免疫肿瘤学的能力。在这里,我们将基于人工智能的高倍空间分析应用于BC组织,研究免疫细胞类型和生物标记物,从而深入了解受免疫疗法反应的TME分子机制。
利用光片显微技术聚焦三维长时程成像
长时程三维成像揭示了复杂的多细胞系统是如何生长和发育的,以及细胞是如何随着时间的推移而移动和相互作用的,从而揭示了发育、疾病和再生方面的重要知识。光片显微镜一次只照射样品的一个薄片,大大减少了光损伤,保护了样品的活性。这种温和的高速技术可在数小时甚至数天内提供清晰的体数据,使研究人员能够实时捕捉生物学的发展过程。